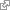SCOPE-chip
The SCOPE-chip captures single cells by partitioning them into hundreds of thousands of microwells on the chip following the Poisson distribution. Afterwards, an excess of Barcoding Beads is added to the microwells of the chip; the diameter of the beads versus that of the microwells ensuring that only one Barcoding Bead falls into each microwell. After cell lysis, Barcoding Beads, each with a unique cell label (Barcode), capture mRNA by binding to the poly (A) tail. Barcoding Beads are subsequently collected from the microwell chip, followed by reverse transcription of the mRNA captured by the Barcoding Beads into cDNA, and subsequent PCR amplification. The amplified cDNA is then fragmented and ligated with sequencing adapters. The end result is an NGS library that is compatible with Illumina sequencing instruments, that can also be run on Pacbio and MGI sequencing platforms with minor modifications. [ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34326696 http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3163-0115 ]
Term info
added_for_HCA
paola
The SCOPE-chip captures single cells by partitioning them into hundreds of thousands of microwells on the chip following the Poisson distribution. Afterwards, an excess of Barcoding Beads is added to the microwells of the chip; the diameter of the beads versus that of the microwells ensuring that only one Barcoding Bead falls into each microwell. After cell lysis, Barcoding Beads, each with a unique cell label (Barcode), capture mRNA by binding to the poly (A) tail. Barcoding Beads are subsequently collected from the microwell chip, followed by reverse transcription of the mRNA captured by the Barcoding Beads into cDNA, and subsequent PCR amplification. The amplified cDNA is then fragmented and ligated with sequencing adapters. The end result is an NGS library that is compatible with Illumina sequencing instruments, that can also be run on Pacbio and MGI sequencing platforms with minor modifications.
GEXSCOPE