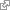nephron
The basic functional unit of the kidney. its chief function is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances like sodium salts by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine. A nephron eliminates wastes from the body, regulates blood volume and blood pressure, controls levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulates blood pH. Its functions are vital to life and are regulated by the endocrine system by hormones such as antidiuretic hormone, aldosterone, and parathyroid hormone.[WP]. [ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9268568 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nephron ]
Term info
- ZFA:0005282
- Wikipedia:Nephron
- NCIT:C13048
- MESH:D009399
- EMAPA:35592
- UMLS:C0027713 (ncithesaurus:Nephron)
- CALOHA:TS-1312
- BTO:0000924
- MA:0000375
- GAID:428
- SCTID:361337001
- EMAPA:28491
- TAO:0002153
- EV:0100384
- FMA:17640
uberon_slim, pheno_slim, vertebrate_core, human_reference_atlas
Functional unit of the kidney that filters waste.[TAO]
In the avian kidney, three types of nephron are identified: mammalian-type nephrons with long and short loops of Henle, and reptilian type nephrons (Gambaryan, 1992)
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/02/Gray1128.png
kidney terms require review for cross-vertebrate compatibility and developmental relationships.
nephroneum, tubulus renalis
mature nephron
uberon
UBERON:0001285
Nephron
http://purl.obolibrary.org/obo/NCBITaxon_9606
Term relations
- Cardinal organ part
- anatomical entity
- contributes to morphology of some kidney
- develops from some primitive nephron
- immediate transformation of some primitive nephron
- part of some uriniferous tubule