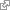optic disc
The optic disc or optic nerve head is the location where ganglion cell axons exit the eye to form the optic nerve. There are no light sensitive rods or cones to respond to a light stimulus at this point. This causes a break in the visual field called 'the blind spot' or the 'physiological blind spot'. The optic nerve head in a normal human eye carries from 1 to 1.2 million neurons from the eye towards the brain. [WP,unvetted]. [ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Optic_disc ]
Synonyms: optic disk
Term info
- UMLS:C0029127 (ncithesaurus:Optic_Disc)
- NCIT:C12760
- EFO:0001974
- Wikipedia:Optic_disc
- EHDAA2:0001307
- FMA:58634
- EMAPA:18238
- SCTID:362518006
- VHOG:0000551
- MESH:D009898
- EHDAA:9077
- MA:0000278
- CALOHA:TS-2153
uberon_slim, efo_slim, pheno_slim
The small blind spot on the surface of the retina. It is the point where the fibers of the retina leave the eye and become part of the optic nerve. [TFD][VHOG]
(...) we reach the inescapable conclusion that the last common ancestor of jawless and jawed vertebrates already possessed an eye that was comparable to that of extant lampreys and gnathostomes. Accordingly, a vertebrate camera-like eye must have been present by the time that lampreys and gnathostomes diverged, around 500 Mya (reference 1); Although the eye varies greatly in adaptative details among vertebrates, its basic structure is the same in all. The human eye is representative of the design typical for a tetrapod (reference 2).[well established][VHOG]
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/ed/Gray879.png
optic disk, optic papilla, physiologic blind spot of mariotte, physiologic blind spot, optic nerve head, optic nerve disc
uberon
UBERON:0001783
Optic disc
Term relations
- Cardinal organ part
- ectoderm-derived structure
- part of some retina
- extends_fibers_into some cranial nerve II