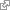internal ear
Complex labyrinthine structure that comprises sensory endorgans specialized for vestibular, auditory, and acoustico-vestibular sensation. [ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internal_ear http://zfin.org/cgi-bin/ZFIN_jump?record=curator http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16217737 ]
Synonyms: inner ear
Term info
- VHOG:0000284
- XAO:0000192
- EHDAA2:0000831
- MIAA:0000145
- MAT:0000145
- NCIT:C12499
- Wikipedia:Internal_ear
- FMA:60909
- UMLS:C1268973 (BIRNLEX:1196)
- ZFA:0000217
- BTO:0000630
- EV:0100361
- UMLS:C0022889 (ncithesaurus:Internal_Ear)
- GAID:871
- CALOHA:TS-0478
- MESH:D007758
- galen:InnerEar
- MA:0000237
- UMLS:C0022889 (BIRNLEX:1196)
- SCTID:181189006
- BIRNLEX:1196
- EMAPA:16194
- EFO:0001363
- SCTID:304982002
- AAO:0000238
- EHDAA:504
- TAO:0000217
uberon_slim, efo_slim, pheno_slim, vertebrate_core
The auditory (hearing) and vestibular (balance) organ of the fish, equivalent to the inner ear of amniotes. (See Anatomical Atlas entry for ear by T. Whitfield.)[TAO]
The labyrinth, or inner ear, evolved very early in vertebrate history and, with many variations in configuration but none of basic design and function, has been retained by all vertebrates.[well established][VHOG]
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/19/Gray923.png
otocyst, auris interna, labyrinth
uberon
UBERON:0001846
Internal ear
Term relations
- multi organ part structure
- ectoderm-derived structure
- part of some ear
- develops from some ear vesicle