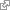falx cerebri
The falx cerebri, also known as the cerebral falx, so named from its sickle-like form, is a strong, arched fold of dura mater which descends vertically in the longitudinal fissure between the cerebral hemispheres. It is narrow in front, where it is attached to the crista galli of the ethmoid; and broad behind, where it is connected with the upper surface of the tentorium cerebelli. Its upper margin is convex, and attached to the inner surface of the skull in the middle line, as far back as the internal occipital protuberance; it contains the superior sagittal sinus. Its lower margin is free and concave, and contains the inferior sagittal sinus. The falx cerebri is known to calcify with age. [ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Falx_cerebri ]
Synonyms: cerebral falx
Term info
- FMA:83967
- UMLS:C0228120 (ncithesaurus:Falx_Cerebri)
- neuronames:1237
- SCTID:279275004
- NCIT:C12890
- Wikipedia:Falx_cerebri
- EMAPA:18551
pheno_slim
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/ff/Falxcerebri.jpg
uberon
UBERON:0006059
Falx cerebri
Term relations
- Cardinal organ part
- ectoderm-derived structure
- part of some dura mater
- develops from some future falx cerebri
- immediate transformation of some future falx cerebri