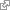Gray matter heterotopia
Heterotopia or neuronal heterotopia are macroscopic clusters of misplaced neurons (gray matter), most often situated along the ventricular walls or within the subcortical white matter. [ COST:neuromig PMID:22427329 PMID:7524438 PMID:25180909 ORCID:0000-0001-5208-3432 ]
Term info
- UMLS:C0008519
- SNOMEDCT_US:128490007
- SNOMEDCT_US:416286003
- MSH:D002828
- SNOMEDCT_US:417338002
Gray matter heterotopia is caused by clumps of grey matter being located in the wrong part of the brain. It is characterized as a type of cortical malformation. The neurons in heterotopia may appear to be normal, except for their mislocation; nuclear studies have shown glucose metabolism equal to that of normally positioned gray matter. The condition causes a variety of symptoms, but usually includes some degree of epilepsy or recurring seizures, and often affects the brain's ability to function on higher levels. Symptoms range from nonexistent to profound, in which case heterotopia can result in severe seizure disorder, loss of motor skills, and mental retardation. Neuronal heterotopia consists of grey matter within the white matter, and the term grey matter heterotopia is more frequently used.
Heterotopia or neuronal heterotopia are macroscopic clusters of misplaced neurons (gray matter), most often situated along the ventricular walls or within the subcortical white matter.
HP:0002281, HP:0007314
Heterotopias, Grey matter heterotopia, Neuronal heterotopia, Gray matter heterotopias, Heterotopia, Grey matter heterotopias
HP:0002282